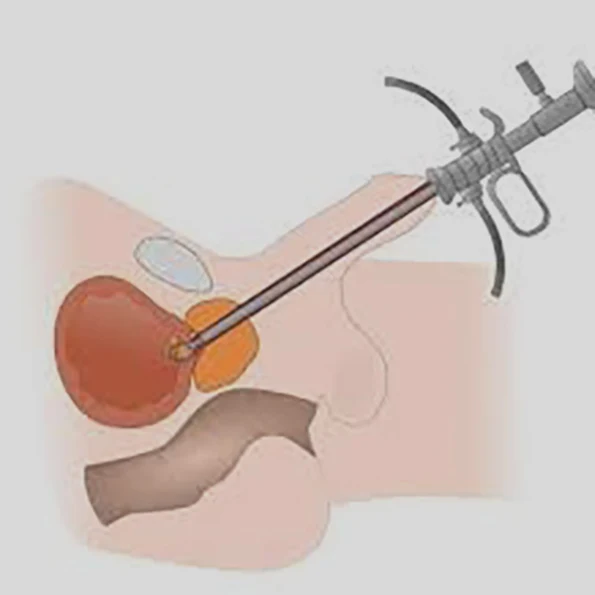
1. Surgery Overview
TURP (Transurethral Resection of the Prostate) is a common surgical procedure used to treat urinary problems caused by an enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). During the procedure, a resectoscope is inserted through the urethra to remove excess prostate tissue, improving urine flow. TURP is considered the gold standard treatment for moderate to severe BPH.
2. Type of Anesthesia
TURP is typically performed under spinal anesthesia (regional) or general anesthesia, depending on the patient’s condition and preference.
3. Possible Risks and Complications
Bleeding
Urinary tract infection (UTI)
Temporary difficulty urinating or urinary retention
Retrograde ejaculation (semen flows into the bladder)
Erectile dysfunction (rare)
Incontinence (usually temporary)
Need for repeat surgery in the future
4. Hospital Stay Duration
The hospital stay is usually 1 to 2 days. A catheter is typically left in place for 1–3 days after surgery to help with urine drainage.
5. Important Post-Operative Care
Drink plenty of fluids to flush the bladder and reduce irritation
Avoid heavy lifting, strenuous activity, and sexual activity for 4–6 weeks
Follow catheter care instructions if discharged with one
Take all prescribed medications, including antibiotics and pain relievers
Monitor for signs of infection or bleeding and report to your doctor if symptoms occur
Attend all follow-up appointments to assess healing and urinary function