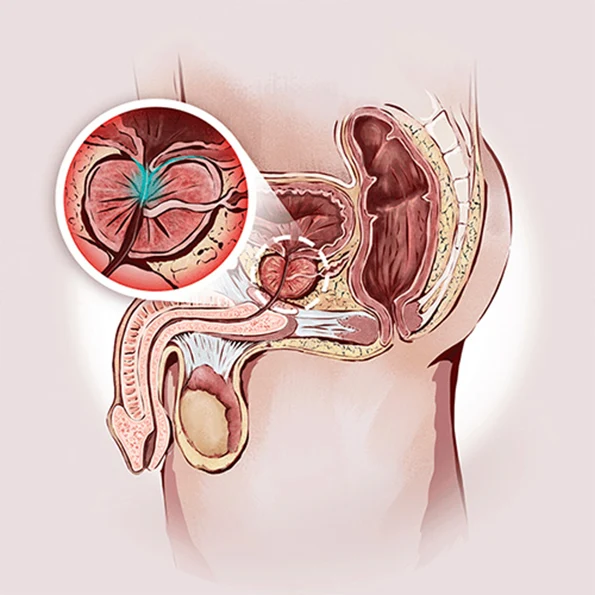
1. Surgery Overview
Prostatectomy is a surgical procedure to remove all or part of the prostate gland. It is most commonly performed to treat prostate cancer or severe benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) that does not respond to other treatments. The main types include:
Radical prostatectomy (removal of the entire prostate and surrounding tissues)
Simple prostatectomy (removal of part of the prostate, usually for BPH)
The procedure can be performed using open surgery or minimally invasive methods such as laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery.
2. Type of Anesthesia
Prostatectomy is performed under general anesthesia. In some cases, spinal or epidural anesthesia may be used in combination for additional pain control during recovery.
3. Possible Risks and Complications
Infection
Bleeding
Injury to nearby structures (bladder, rectum, nerves)
Urinary incontinence
Erectile dysfunction
Blood clots
Scarring or narrowing of the urethra
4. Hospital Stay Duration
Hospital stay is usually 1 to 3 days for minimally invasive surgery and up to 5 days for open prostatectomy, depending on the patient’s condition and surgical approach.
5. Important Post-Operative Care
A urinary catheter is typically left in place for 1–2 weeks after surgery
Drink plenty of fluids to flush the bladder and reduce the risk of infection
Avoid strenuous activity and heavy lifting for several weeks
Take prescribed medications for pain and bladder control
Attend follow-up appointments to monitor recovery and urinary function Pelvic floor exercises (Kegels) may be recommended to improve urinary control