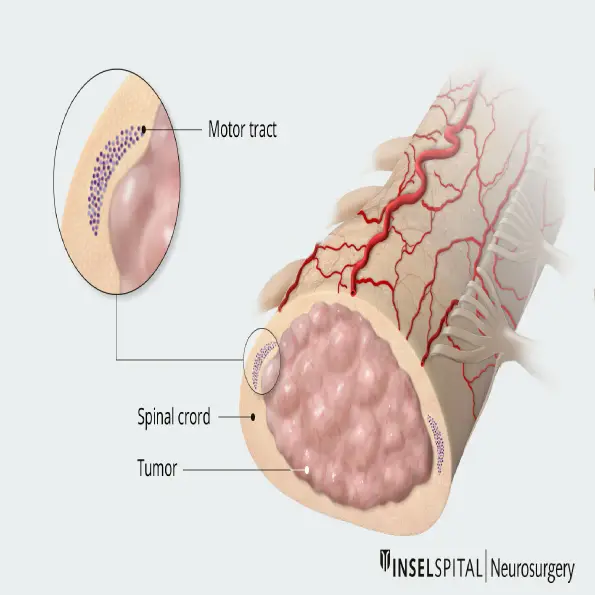
1. Procedure Overview
Intramedullary spinal cord tumor surgery is performed to remove tumors located within the spinal cord. These tumors can cause symptoms such as pain, weakness, numbness, or difficulty with movement. Surgical removal of these tumors is often necessary to relieve pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. The procedure typically involves:
Tumor Resection: The surgeon removes as much of the tumor as possible while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Intramedullary Approach: The surgery is usually performed through a posterior (back) approach, where the vertebrae are carefully opened to access the spinal cord.
Microsurgical Techniques: In many cases, a microscope is used to enhance precision and preserve spinal cord function.
The goal is to remove the tumor while maintaining spinal cord integrity.
2. Type of Anesthesia
This surgery is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is unconscious and pain-free during the procedure.
3. Possible Risks and Complications
Infection
Bleeding
Nerve or spinal cord injury, leading to weakness, sensory loss, or paralysis
Spinal fluid leak
Scar tissue formation around the spinal cord
Anesthesia-related complication
4. Hospital Stay Duration
The typical hospital stay is 5 to 7 days, depending on the surgery’s complexity and the patient’s recovery.
5. Important Post-Operative Care
Pain management and wound care
Monitoring of neurological function
Physical therapy to regain strength and mobility
Gradual return to normal activities
Follow-up imaging (MRI, CT) to ensure tumor removal and spinal cord healing
6. Possibility of Recurrence
The likelihood of tumor recurrence depends on several factors, including the type of tumor, whether it was fully resected, and the tumor’s grade. Some intramedullary tumors, such as gliomas, have a higher risk of recurrence due to their infiltrative nature. Regular follow-up with MRI scans is essential to monitor for any signs of tumor regrowth. For certain types of tumors, recurrence is more likely within the first 5 years after surgery, but this can vary.