1. Procedure Overview
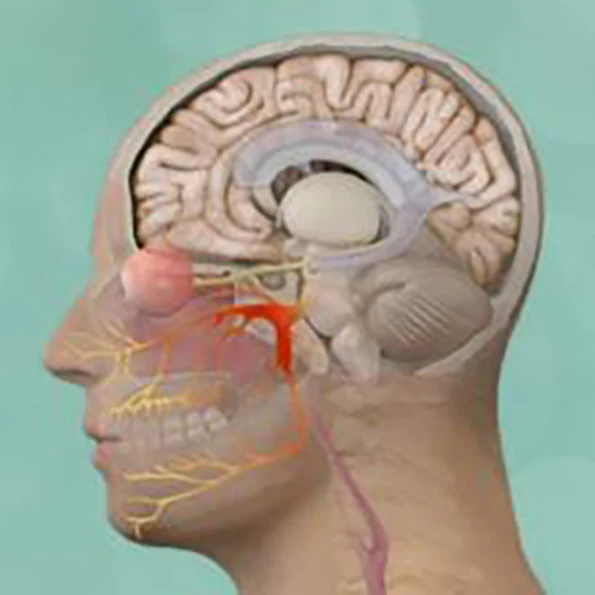
Hemifacial spasm surgery is typically performed to treat involuntary muscle contractions or twitching on one side of the face, caused by irritation or compression of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII). The most common and effective surgical treatment is:
Microvascular Decompression (MVD): Through a small opening behind the ear, the surgeon identifies the blood vessel compressing the facial nerve and places a soft cushion between them. This relieves the pressure and allows the nerve to function normally.
MVD offers long-term relief and is often recommended when medication or botulinum toxin injections are no longer effective.
2. Type of Anesthesia
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is completely asleep and pain-free during the procedure.
3. Possible Risks and Complications
Hearing loss (due to proximity to auditory nerve)
Facial weakness or numbness
Infection
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak
Stroke (rare)
Anesthesia-related complications
4. Hospital Stay Duration
Patients typically stay in the hospital for 2 to 4 days, depending on recovery progress and any post-operative complications.
5. Important Post-Operative Care
Close monitoring in the ICU for the first 24 hours
Pain and swelling management
Follow-up MRI or imaging if necessary
Avoiding heavy lifting or intense activity for a few weeks
Long-term follow-up to assess symptom relief and detect any recurrence.