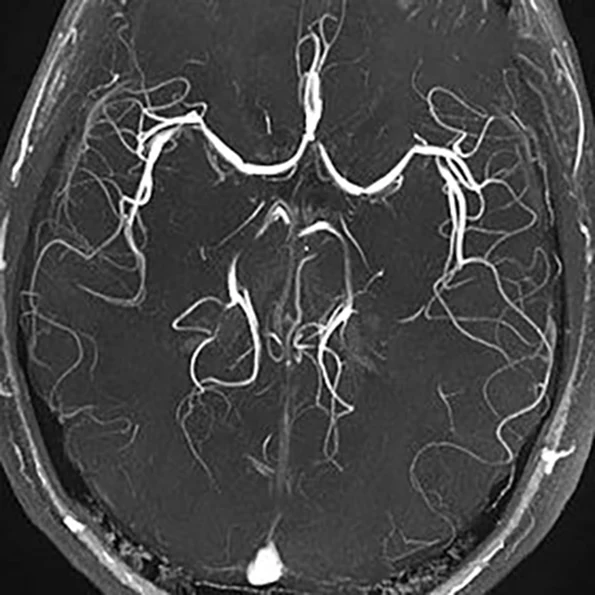
1. Procedure Overview
Brain angiography, also known as cerebral angiography, is a diagnostic imaging procedure used to visualize the blood vessels in the brain. It helps detect abnormalities such as aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), stenosis, or blockages. The procedure involves inserting a catheter, typically through the femoral artery in the groin, and guiding it to the cerebral arteries to inject a contrast dye. X-ray images are then taken to assess the cerebral vasculature. The procedure usually takes between 1 to 3 hours.
2. Type of Anesthesia
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia at the catheter insertion site. Sedation may also be administered to help the patient relax during the procedure.
3. Possible Risks and Complications
Bleeding or hematoma at the catheter insertion site
Allergic reaction to the contrast dye
Infection
Stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)
Blood vessel damage
Kidney damage, especially in patients with pre-existing kidney conditions
4. Hospital Stay Duration
Brain angiography is typically an outpatient procedure. Patients are usually monitored for several hours after the procedure and can go home the same day, provided there are no complications. In some cases, an overnight hospital stay may be required.
5. Important Post-Procedure Care
Keep the catheter insertion site clean and dry
Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting for at least 2 to 3 days
Monitor for signs of infection or bleeding at the insertion site
Stay hydrated to help flush the contrast dye from the body
Follow up with your healthcare provider as recommended.
Brain endoscopy: Estimated price: 6,000 – 8,000 $
1. Procedure Overview
Neuroendoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that utilizes a thin, flexible tube called an endoscope, equipped with a camera and light source, to access and treat conditions within the brain, ventricles, and spinal cord. This approach allows neurosurgeons to reach areas that are difficult to access with traditional open surgery, often through small incisions or natural openings, such as the nose or mouth. Common applications include the treatment of hydrocephalus, brain cysts, and certain types of brain tumors. (mercy.com)
2. Type of Anesthesia
The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia, ensuring the patient remains unconscious and free from pain during the surgery. In some cases, local anesthesia may be used, depending on the specific procedure and patient condition. (madeforthismoment.asahq.org)
3. Possible Risks and Complications
While neuroendoscopy is less invasive than traditional brain surgery, it carries potential risks, including:
Bleeding
Infection
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks
Damage to surrounding brain structures
Anesthetic complications
These risks are generally lower compared to open brain surgery but should be discussed with the surgical team. (pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
4. Hospital Stay Duration
The length of hospital stay varies based on the specific procedure and patient recovery. For less invasive procedures like neuroendoscopy, patients may stay in the hospital for 1 to 3 days. However, the duration can be longer if complications arise or if additional treatments are required. (my.clevelandclinic.org)
5. Important Post-Operative Care
Post-operative care is crucial for recovery and may include:
Monitoring for signs of infection or bleeding
Managing pain and discomfort
Ensuring proper positioning to prevent complications
Gradual resumption of normal activities as advised by the healthcare team
Patients are typically advised to follow up with their healthcare provider to monitor healing and address any concerns. (pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)