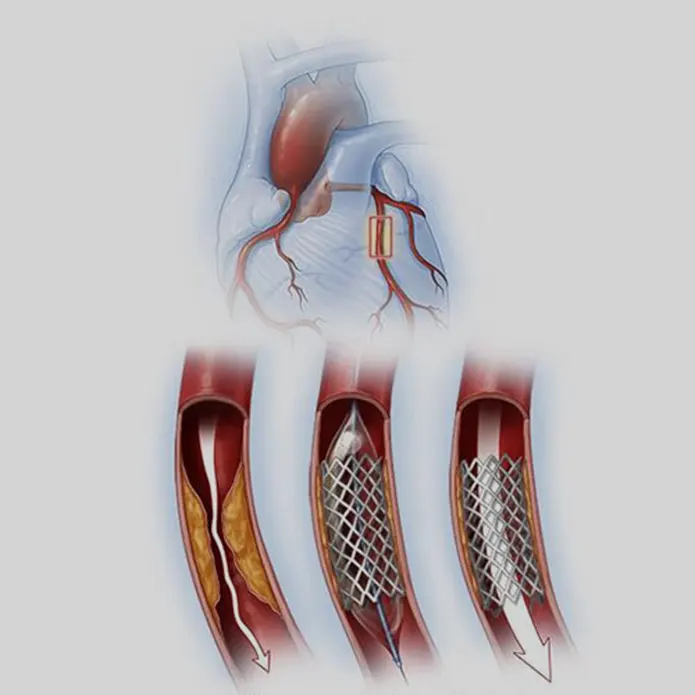
1. Surgery Overview
Complex coronary angioplasty, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a procedure used to open narrowed or blocked coronary arteries, especially in patients with complicated or multiple blockages. It involves inserting a catheter through a blood vessel (usually in the groin or wrist) to reach the heart. A balloon is inflated at the blockage site to open the artery, and one or more stents (tiny mesh tubes) are placed to keep the artery open. Complex angioplasty may involve treating bifurcated lesions, chronic total occlusions, or heavily calcified arteries, and may require advanced tools like rotational atherectomy.
2. Type of Anesthesia
The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia with sedation. The patient remains awake but relaxed, and the insertion area is numbed. In rare or emergency cases, general anesthesia may be used.
3. Possible Risks and Complications
Bleeding or hematoma at the catheter insertion site
Blood vessel damage
Allergic reaction to the contrast dye
Irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias)
Heart attack or stroke during the procedure
Re-narrowing (restenosis) or re-blockage of the treated artery
Blood clots forming in the stent (stent thrombosis)
Kidney damage from the contrast dye, especially in patients with kidney disease
Perforation of the artery (rare)
Complications related to anesthesia
4. Hospital Stay Duration
Patients usually stay in the hospital for 1 to 2 days after a complex angioplasty, depending on their condition and response to the procedure.
A longer stay may be required if complications occur or if the patient has other serious medical conditions.
5. Important Post-Operative Care
Rest and avoid heavy physical activity for about a week or as advised by the doctor
Keep the catheter insertion site clean and dry; watch for swelling, bleeding, or signs of infection
Take all prescribed medications, including antiplatelet drugs (such as aspirin and clopidogrel) to prevent blood clots
Maintain a heart-healthy lifestyle with diet, exercise, and smoking cessation
Monitor for chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness, and report them immediately to a doctor
Attend regular follow-up visits and cardiac rehabilitation, if recommended.